- Dehydrogenase
- Classification:
- Cofactors:
- Classical members:
- Lactate dehydrogenase
- Alcohol dehydrogenase
- Glucose 6 phosphate dehydrogenase
- Pyruvate dehydrogenase
- Aldehyde dehydrogenase
- Succinate dehydrogenase
- Malate dehydrogenase
- Glutamate dehydrogenase
- Isocitrate dehydrogenase
- Glu/Leu/Phe/Val dehydrogenase
|
|
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) definition
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide or NAD+ is the cofactor or coenzyme for most dehydrogenases. NAD+ is the oxidised form of NADH and vice versa, NADH id the reduced form of NAD+. NAD+ is a source for NADP+ biosynthesis by NAD+-kinase with subsequent energy transduction from ATP.
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) basic
- Molecular formula: C21H27N7O14P2
- Molecular weight: 663.425 Da
- IUPAC name 1: [(2R,3R,4S)-5-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxy-oxolan-2-yl]methoxy-[[(3R,4S)-4-(5-carbamoylpyridin-1-yl)-3,4-dihydroxy-oxolan-2-yl]methoxy-oxido-phosphoryl]oxy-phosphinic acid
- IUPAC name 2: [[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(5-aminocarbonylpyridin-1-yl)-3,4-dihydroxy-oxolan-2-yl]methoxy-oxido-phosphoryl]oxy-[[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxy-oxolan-2-yl]methoxy]phosphinic acid
- Appearance: White crystalline solid
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) structure
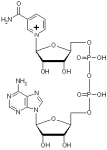
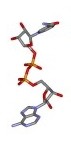
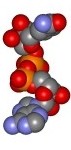

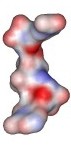
Different representation of the Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) structure. All structures were derived from the NAD+ coordinates from the structure of Aldehyde Dehydrogenase from Bovine mitochondria complex with NAD and Samarium (1A4Z.pdb). Click preview to see full resolution stereo picture.
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) synthesis pathway
In living organisms NAD+ can be synthesized by two different pathways. These pathways are merged by formation of nicotinate D-ribonucleotide. First pathway, also called kynurenine pathway is started from essential amino acid Tryptophan. Lack of Tryptophan on the diet can cause the Nicotinamide deficiently disease pellagra. Second pathway is started from Vitamin B3 (niacin, nicotinic acid). This vitamin is also essential.
Tryptophan pathway
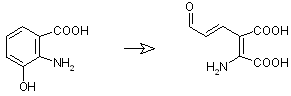
Conversion of L-Kynurenine to 3-Hydroxyanthranilic acid can be done by two different ways:
via 3-Hydroxykynurenine
and via Anthranilic acid
After this small difference in the pathway, the last steps are common:
|
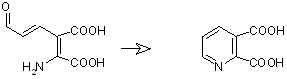
3-Hydroxyanthranilic acid -> 2-amino-3-carboxymuconate semialdehyde catalyzed by 3-Hydroxyanthranilic acid oxidase, EC 1.13.11.6
Download ISIS Draw source file here
|
|
2-amino-3-carboxymuconate semialdehyde -> Quinolinic acid, This is a non-enzymatic spontaneous step of catalysis
Download ISIS Draw source file here
|
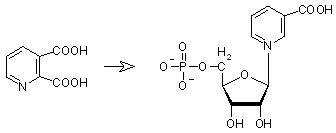
|
pyridine-2,3-dicarboxylate (Quinolinic acid) + 5-phospho-alpha-D-ribose 1-diphosphate -> nicotinate D-ribonucleotide + diphosphate + CO2, catalyzed by nicotinate-nucleotide diphosphorylase (nicotinate-nucleotide:diphosphate phospho-alpha-D-ribosyltransferase), EC 2.4.2.19
Download ISIS Draw source file here
|
Vitamin B3 (niacin, nicotinic acid) pathway
This pathway is started from Vitamin B3 (nicotinate).
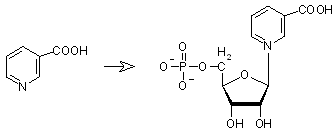
|
Nicotinate (Vitabin B3) + 5-phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate -> nicotinate D-ribonucleotide + diphosphate, catalyzed by nicotinate phosphoribosyltransferase (icotinate-nucleotide:diphosphate phospho-alpha-D-ribosyltransferase), EC 2.4.2.11
Download ISIS Draw source file here
|
Common steps of NAD+ biosynthesis.
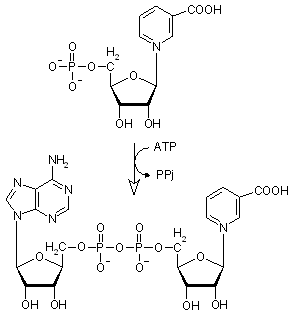
|
Nicotinate D-ribonucleotide + ATP -> deamido-NAD+ + diphosphate, catalyzed by nicotinate-nucleotide adenylyltransferase (ATP:nicotinate-ribonucleotide adenylyltransferase), EC 2.7.7.18
Download ISIS Draw source file here
|
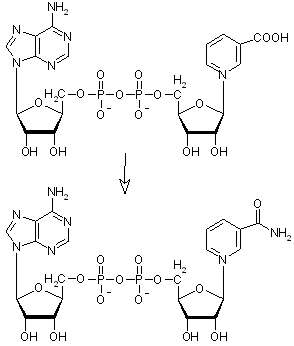
|
deamido-NAD+ -> NAD+
This reaction can be catalysed by two different enzymes :
- deamido-NAD+:L-glutamine amido-ligase (AMP-forming) EC 6.3.5.1 or NAD+ synthase (glutamine-hydrolysing) via reaction:
ATP + deamido-NAD+ + L-glutamine + H2O => AMP + diphosphate + NAD+ + L-glutamate
- deamido-NAD+:ammonia ligase (AMP-forming) EC 6.3.1.5 or NAD+ synthase via reaction:
ATP + deamido-NAD+ + NH3 => AMP + diphosphate + NAD+
Download ISIS Draw source file here
|
NAD+ and NADH
The overall involvement of Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate into the living cell processes is illustrated on Nicotinamide nucleotides in catabolism and biosynthesis scheme.
The reaction of NADH oxidation to NAD+ mainly presents in the electron-transport chain pathways:
The first reaction in the electron-transport chain is reaction NADH + H+ + ubiquinone => NAD+ + ubiquinol catalyzed by NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase EC 1.6.5.3 (other names: NADH2 dehydrogenase (ubiquinone); NADH-Q6 oxidoreductase; electron transfer complex I; NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase complex; NADH-ubiquinone-1 reductase; reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-coenzyme Q reductase; NADH-ubiquinone reductase; NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase; NADH-CoQ oxidoreductase; NADH-coenzyme Q reductase; NADH-CoQ reductase; NADH coenzyme Q1 reductase; NADH-coenzyme Q oxidoreductase; mitochondrial electron transport complex I; mitochondrial electron transport complex 1; DPNH-ubiquinone reductase; DPNH-coenzyme Q reductase; dihydronicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-coenzyme Q reductase; complex I (NADH:Q1 oxidoreductase); ubiquinone reductase; type 1 dehydrogenase; complex 1 dehydrogenase; coenzyme Q reductase; complex I (electron transport chain); complex I (mitochondrial electron transport); NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone)).
|