- Dehydrogenase
- Classification:
- Cofactors:
- Classical members:
- Lactate dehydrogenase
- Alcohol dehydrogenase
- Glucose 6 phosphate dehydrogenase
- Pyruvate dehydrogenase
- Aldehyde dehydrogenase
- Succinate dehydrogenase
- Malate dehydrogenase
- Glutamate dehydrogenase
- Isocitrate dehydrogenase
- Glu/Leu/Phe/Val dehydrogenase
|
|
Navigation: Go back to the NAD+/NADH description; NADP+/NADPH description
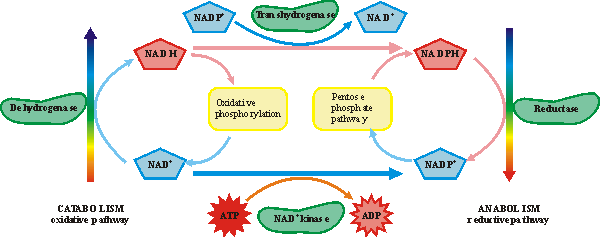
Nicotinamide dinucleotides in biosynthesis
NAD+ is the main cofactor for most dehydrogenases, the main pathway for NADH oxidation is the electron transport and oxidative phosphorilation. NADPH is usually involved as a cofactor for reductases, enzymes that catalyse substrate reduction. The main pathway for NADP+ reduction is the Pentose phosphate pathway. NADPH synthesized from NADH via mitochondrial energy-linked transhydrogenase. NADP+ synthesized from NAD+ by NAD+-kinase with subsequent energy transduction from ATP.
Navigation: Go back to the NAD+/NADH description; NADP+/NADPH description
|